Table of Contents
- Donald Trump's tariffs: What's going on and what does it all mean? | US ...
- Trump tariffs: Why 'it's complicated' for Canadian commercial brokers
- tariff and its types | PPT
- What are tariffs? Definition and meaning - Market Business News
- You will pay for Donald Trump’s tariffs. Here’s proof | CNN Business
- Trump tariffs explained: Will they raise costs for Americans? | wnep.com
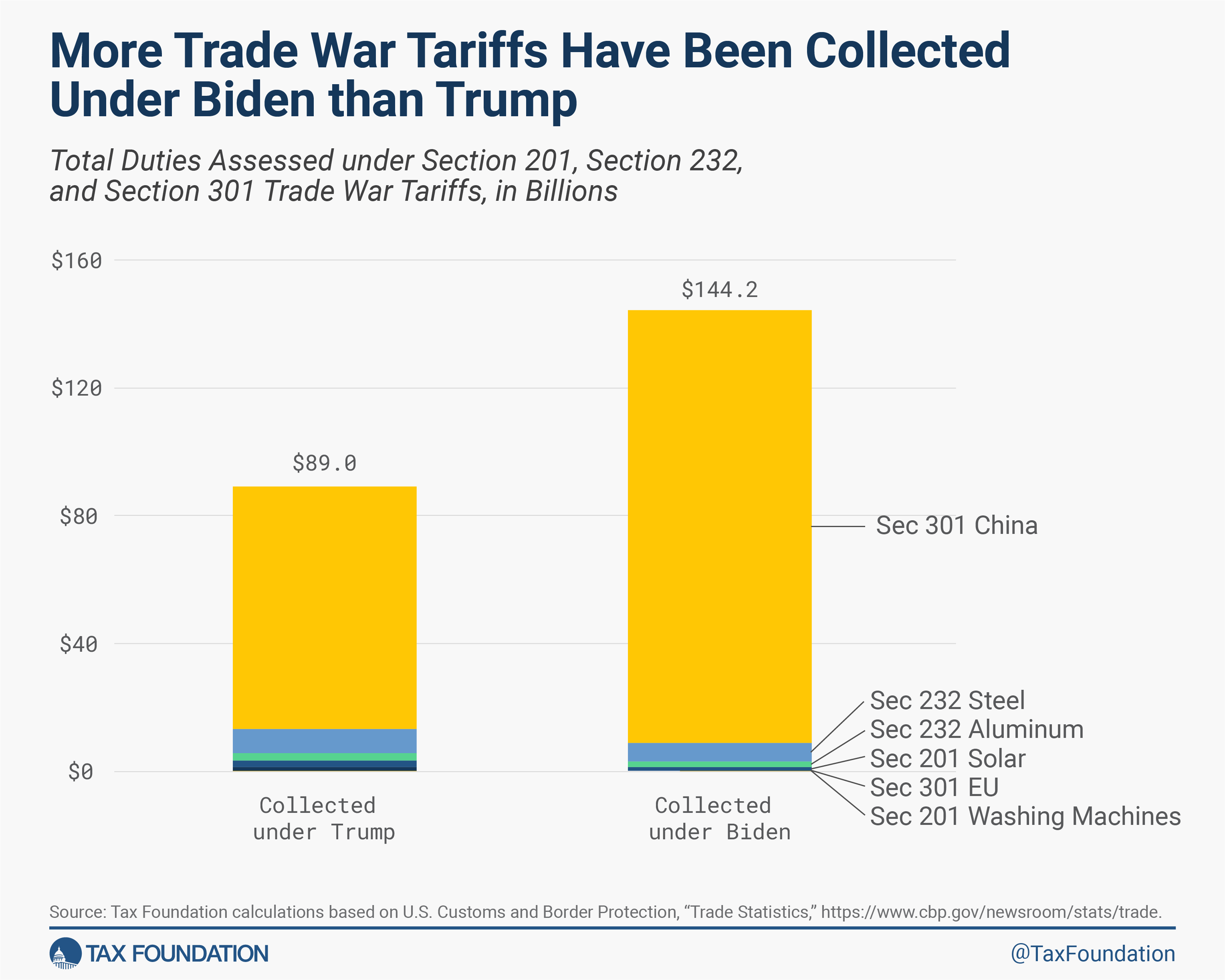
- Americans Are Still Paying for the Trump-Biden Tariffs - Taxes Alert
- A Tariff Is a Tax - Econlib
- types of tariffs, advantage of tariff, how tariff work,.pdf
- Understanding the Tariffs and Customs Fees of Your Destination Country ...

When it comes to international trade, tariffs are a crucial aspect that can significantly impact the global economy. In recent years, tariffs have been a topic of discussion among policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. But what exactly are tariffs, and how do they work? In this article, we will delve into the world of tariffs, exploring their definition, types, and effects on the economy.


What are Tariffs?
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on imported goods and services from other countries. The primary purpose of tariffs is to protect domestic industries by making foreign products more expensive for consumers. This can help to level the playing field for local businesses, which might otherwise struggle to compete with cheaper imports. Tariffs can be levied on a wide range of products, including agricultural goods, manufactured goods, and even services.


Types of Tariffs

There are several types of tariffs, each serving a specific purpose. Some of the most common types of tariffs include:

- Ad valorem tariffs: These tariffs are levied as a percentage of the imported product's value.
- Specific tariffs: These tariffs are levied as a fixed amount per unit of the imported product.
- Compound tariffs: These tariffs combine ad valorem and specific tariffs, with a fixed amount per unit plus a percentage of the product's value.

How Tariffs Work
When a country imposes a tariff on an imported product, it increases the cost of that product for consumers. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the product, as consumers may opt for cheaper alternatives. The revenue generated from tariffs is typically collected by the government and can be used to fund various public projects and initiatives.
For example, if a country imposes a 10% tariff on imported cars, the price of those cars will increase by 10%. This means that if a car costs $10,000, the tariff would add $1,000 to the price, making the total cost $11,000. The $1,000 tariff would be collected by the government, while the consumer would pay the increased price.

Effects of Tariffs on the Economy
Tariffs can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. On the positive side, tariffs can:
- Protect domestic industries and jobs
- Generate revenue for the government
- Encourage domestic production and self-sufficiency
However, tariffs can also have negative effects, including:
- Increasing prices for consumers
- Reducing trade and economic growth
- Leading to retaliatory tariffs from other countries
In conclusion, tariffs are an essential aspect of international trade, and understanding how they work is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals. While tariffs can have both positive and negative effects on the economy, they are an important tool for governments to protect domestic industries and generate revenue. As the global economy continues to evolve, the role of tariffs will remain a vital component of international trade policies.
Source: AP News
Note: The article is written in a way that is easy to understand, and the HTML format is used to make it SEO-friendly. The title is new and descriptive, and the headings and subheadings are used to break up the content and make it easier to read. The article is approximately 500 words and includes a brief summary of what tariffs are, how they work, and their effects on the economy.